Iliotibial Band Syndrome, commonly referred to as IT Band Syndrome or ITBS, is a painful overuse injury that affects the iliotibial band, a thick band of fibrous tissue that runs along the outside of the thigh from the hip to the shin. ITBS is a common condition among runners and athletes, but it can also affect individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive knee bending and flexing.
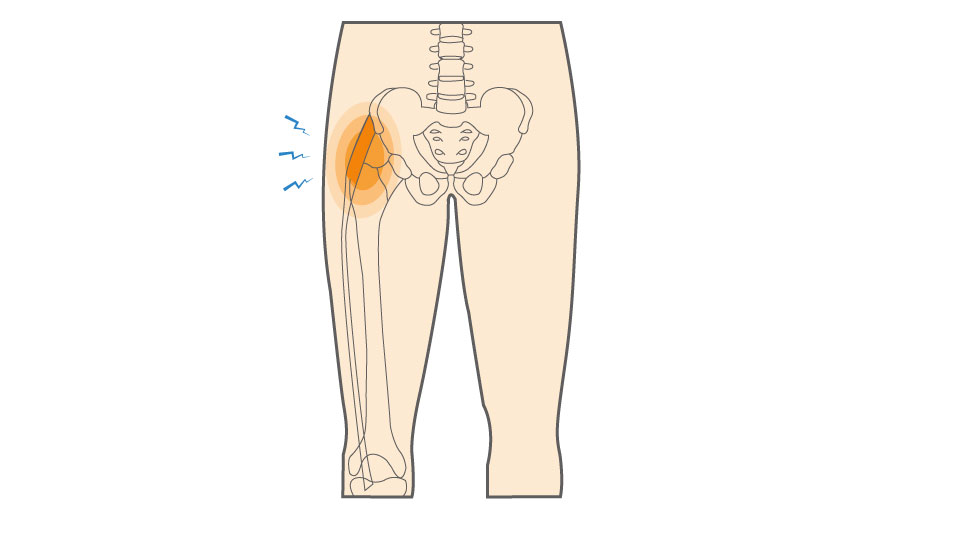
Causes:
Repetitive Motion: IT Band Syndrome is often caused by repetitive motion, such as running or cycling, where the iliotibial band repeatedly rubs against the outer part of the knee joint.
Training Errors: Overtraining, sudden increases in training intensity or volume, or improper training techniques can increase the risk of developing ITBS.
Muscle Imbalances: Weakness or imbalance in the hip and thigh muscles can alter the mechanics of the hip and knee joints, leading to IT Band Syndrome.
Biomechanical Factors: Anatomical factors like leg length discrepancies or abnormal foot arches can contribute to ITBS.
Symptoms:
Pain: The hallmark symptom of IT Band Syndrome is pain on the outer side of the knee or hip. The pain may be sharp and intense and can worsen during activities like running, climbing stairs, or sitting for extended periods with the knee bent.
Swelling: Some individuals may experience swelling or inflammation around the affected area.
Snapping Sensation: In some cases, a snapping or popping sensation may be felt as the iliotibial band moves over the bony prominence of the hip or knee.
Diagnosis:
Dr. Fahad can diagnose IT Band Syndrome based on a physical examination and a review of the patient's medical history. Imaging studies like X-rays or MRI scans are typically not necessary but may be used to rule out other potential causes of knee pain.
Treatment Options:
Rest: The first step in treating IT Band Syndrome is to rest and avoid activities that aggravate the condition. This allows the inflamed tissue to heal.
Ice: Applying ice to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation. Ice should be applied for 15-20 minutes at a time, several times a day.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is often recommended to improve muscle strength, flexibility, and alignment. Specific exercises can target the hip and thigh muscles to alleviate stress on the iliotibial band.
Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Non-prescription anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation, but they should be used under a healthcare provider's guidance.
Bracing or Taping: Some individuals benefit from wearing a knee brace or using kinesiology tape to provide support to the affected area.
Corticosteroid Injections: In severe cases with significant inflammation, a corticosteroid injection may be considered to reduce inflammation and pain.
Prevention:
To prevent IT Band Syndrome or reduce the risk of recurrence, individuals should:
Ensure proper training techniques and gradual increases in exercise intensity.
Incorporate strength and flexibility exercises into their fitness routine, especially focusing on the hip and thigh muscles.
Use appropriate footwear and consider orthotics if necessary.
Pay attention to any early signs of discomfort or pain and seek treatment promptly.
IT Band Syndrome can be a challenging condition to manage, but with the right treatment and preventive measures, most individuals can recover and return to their regular activities.


