What is Calcific Tendinitis?
Calcific tendinitis is a condition where calcium deposits form in the tendons of the shoulder, typically within the rotator cuff. This buildup of calcium can cause inflammation, irritation, and significant pain. The exact cause is not fully understood, but it is thought to result from a combination of wear and tear, aging, and cellular changes in the tendons.
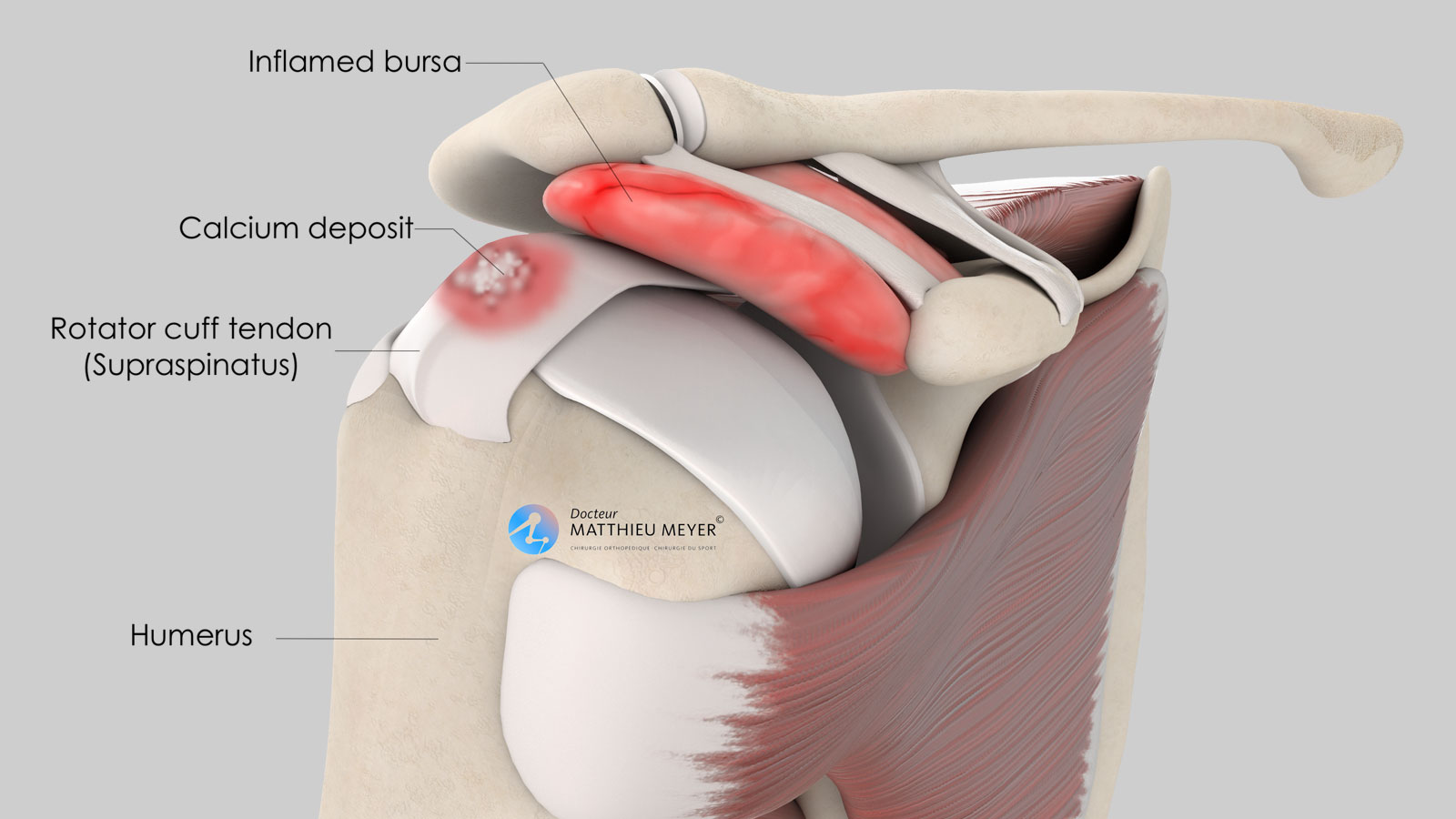
Who is at Risk?
Calcific tendinitis most commonly affects adults between the ages of 30 and 60, and is more prevalent in women than in men. While the condition can develop without a clear reason, certain factors may increase the risk, including:
- Repetitive shoulder motions (due to work or sports)
- Previous shoulder injuries
- Degenerative conditions in the tendons
Symptoms of Calcific Tendinitis:
The calcium deposits may not cause any symptoms at first. However, as they grow or when they become inflamed, patients may experience:
- Sudden or intense shoulder pain
- Difficulty moving the shoulder
- Pain that radiates down the arm
- Pain that worsens at night or with shoulder movement
- Shoulder stiffness or weakness
In severe cases, the pain can be debilitating, significantly limiting daily activities.

How is Calcific Tendinitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination to assess pain, range of motion, and tenderness in the shoulder. Imaging studies such as X-rays or ultrasound are often used to confirm the presence of calcium deposits. MRI scans may be recommended if additional issues like rotator cuff tears are suspected.
Treatment Options:
The treatment for calcific tendinitis depends on the severity of the condition and the patient’s response to initial therapies. The goal is to reduce pain and inflammation while restoring shoulder function. Common treatment options include:
Non-Surgical Treatments:
- Rest and Activity Modification: Limiting activities that aggravate the shoulder can help reduce pain.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Over-the-counter or prescription medications can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Specific exercises to strengthen the shoulder and improve range of motion.
- Corticosteroid Injections: To reduce inflammation and provide temporary relief from pain.
- Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy (ESWT): A non-invasive treatment that uses sound waves to break down the calcium deposits.
Surgical Treatments:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery where small instruments are used to remove the calcium deposits.
- Open Surgery: In rare cases, open surgery may be needed for larger deposits or complex conditions.
Recovery and Prognosis:
Recovery times vary depending on the treatment used. Patients who undergo non-surgical treatments typically see improvement within weeks to months, especially with consistent physical therapy. Surgical recovery may take longer but usually results in significant pain relief and restored function.
Most patients fully recover from calcific tendinitis, though there is a chance of recurrence. Regular follow-ups and shoulder strengthening exercises are important to prevent future problems.
When to See a Doctor?
If you are experiencing persistent shoulder pain or difficulty with movement, it’s important to seek medical attention. Early diagnosis and treatment can prevent the condition from worsening and help restore normal shoulder function more quickly.
Contact Us
If you have any questions about calcific tendinitis or would like to schedule a consultation, please Contact Us.


